A. M.2 (formerly known as NGFF) is a standard for a computer expansion card socket, and the cards that can go into it. M.2 – Wikipedia
M.2 cards are named after their size: the most popular is M.2 2280 – 22 mm wide x 80 mm long. All 22 mm wide cards fit the same basic M.2 socket,but they are keyed with slots in the connector edge to differentiate between different functions of cards.
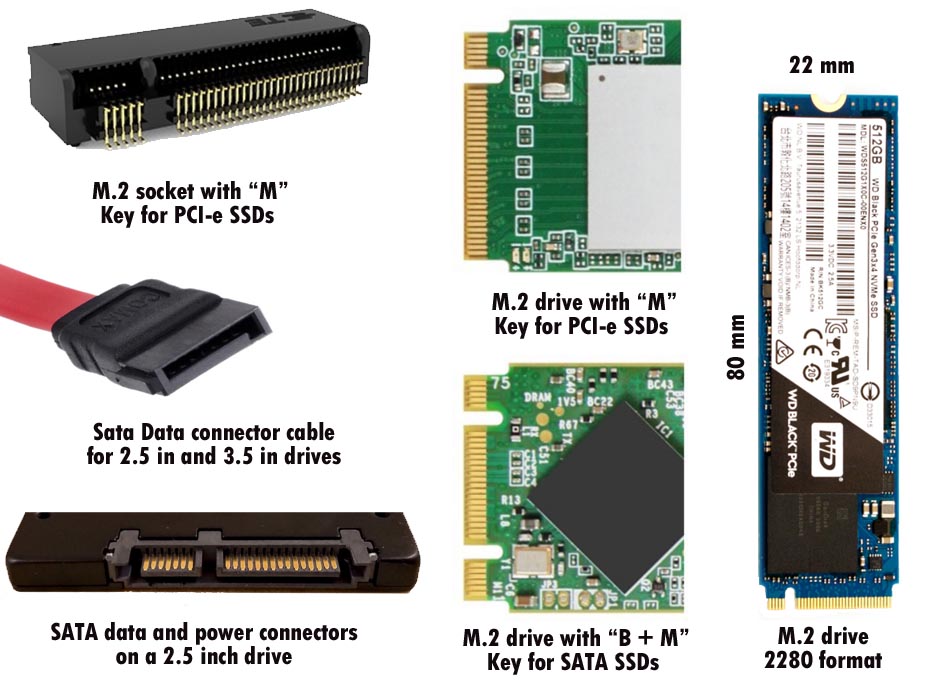
SATA and PCI-e (PCI Express) are both computer bus interfaces for data communication to a storage device.
NVMe (NVM Express) is a logical device interface that is specified for PCI-e devices in the M.2 socket, so “M.2 PCI-e” and “M.2 NVMe” are sometimes used interchangeably. SATA drives use the previous ACHI logical device interface.
SATA devices can come in a variety of physical packages, including 2.5 inch drive, 3.5 inch drive, 5.25 inch optical drive, mSATA socket, or M.2 socket.
M.2 storage devices are designed to work with either the SATA or the PCI-e NVMe standard but not both.
The M.2 slots on a computer motherboard may be SATA only, PCI-e only, or may support drives of both both interfaces: you have to check the documentation or the labeling on the motherboard itself.
Speeds: SATA drives are limited to the maximum SATA bandwidth of 6 Gbps (about 600 MBps). PCI-e Gen3 x4 lane NVMe drives are limited to a theotetical maximum of 3,940 MBps. The newest products shipping with PCI-3 Gen4 x4 lane interfaces have a theoretical maximum of 8000 MBps
